JupyterLab IDE
Overview
The JupyterLab Interactive Development Environment (IDE) capacity within the APEx Project Environments primarily leverages the power of the JupyterLab software.
This APEx tailored User Workspace allows users to maintain a familiar environment and rich feature set while benefiting from the power and resources of server-side computing. This is particularly advantageous for those working on resource-intensive tasks or needing access to a consistent development environment from various locations and devices.
The server-based nature ensures that developers are not constrained by their local machine’s hardware capabilities, allowing them to harness the computational power of remote servers.
Tailored specifically for EO tasks, this environment furnishes developers with an array of tools and libraries fine-tuned for programming languages and productivity plugins or extensions.
Software Architecture
The JupyterLab setup encapsulates a web-based interactive development environment for Jupyter notebooks, code, and data. It is the user interface for Project Jupyter, offering a flexible user interface and more features than the classic notebook UI. It is a web application providing a development environment in which processing algorithms and services can be developed, tested, and debugged.
JupyterLab supports execution environments (called “kernels”) in several dozen languages, including Julia, R, Haskell, Ruby, and Python (via the IPython kernel). It seamlessly adapts to containerised environments, enabling developers to create, test, and deploy applications within isolated, replicable, and consistent environments, ensuring consistent behaviour across development, staging, and production phases.
Key Features
The APEx JupyterLab IDE includes several features that make it suitable for both individual researchers and teams working on EO research and applications.
- Customisable workspaces
Configure your workspace with tools and settings tailored to your specific needs, including debugging tools, data analysis, and data visualisation, as well as a plethora of extensions for JupyterLab from the PyPl.org registry. - EO-focused tools
Access integrated libraries like SNAP and GDAL, which are specifically designed for Earth observation tasks. - Support for every major programming language
Native support for over 40 preinstalled execution environments (called “kernels”) including Python, R, Julia, Scala, Haskell and Ruby, complemented by a vast repository of additional kernels maintained by the open source software community with various levels of support. - Remote development and collaborative work
Leverage integrated Git support, allowing team members to work on the same project by tracking changes and merging updates, helping to keep the code organized while avoiding conflicting code changes.
Showcase Scenarios
The APEx JupyterLab IDE supports a variety of use cases, making it an essential tool for developers, researchers, and data scientists within the EO community. Some typical scenarios include:
- Algorithm Development and Testing
Researchers and developers can write, test, and debug new algorithms for processing satellite imagery or other EO data. For instance, a user might develop a script to detect deforestation using multi-temporal satellite images. To support the productivity of developers, both the JupyterLab solution use a mechanism of extensions.
There is no GitHub Copilot extension available yet for JupyterLab.
See the Code Server IDE page for more details on CoPilot extensions.
Collaborative Projects
Teams can work collaboratively on projects, sharing code and resources in real-time. A group of data scientists might collaboratively develop a machine-learning model to predict crop yields based on various data inputs.Data Science Notebooks
The term “Notebook” usually covers two different concepts, either the user-facing application to edit code and text (this originates from Project Jupyter‘s software product initially branded “Jupyter Notebooks”, nowadays “JupyterLab”), or more commonly the underlying file format which is interoperable across many IDE software solutions. Both solutions proposed for APEx, Code Server, and JupyterLab have multi-kernel language support (python, R, Ruby, …). Code Server supports local development of Jupyter Notebooks: the Jupyter extension for VS Code is a very popular extension in the VS Code Marketplace. JupyterLab is a very popular tool within the Open Science community for working with notebooks, with its native support for data science, data visualisation and reproducible environments.
Examples
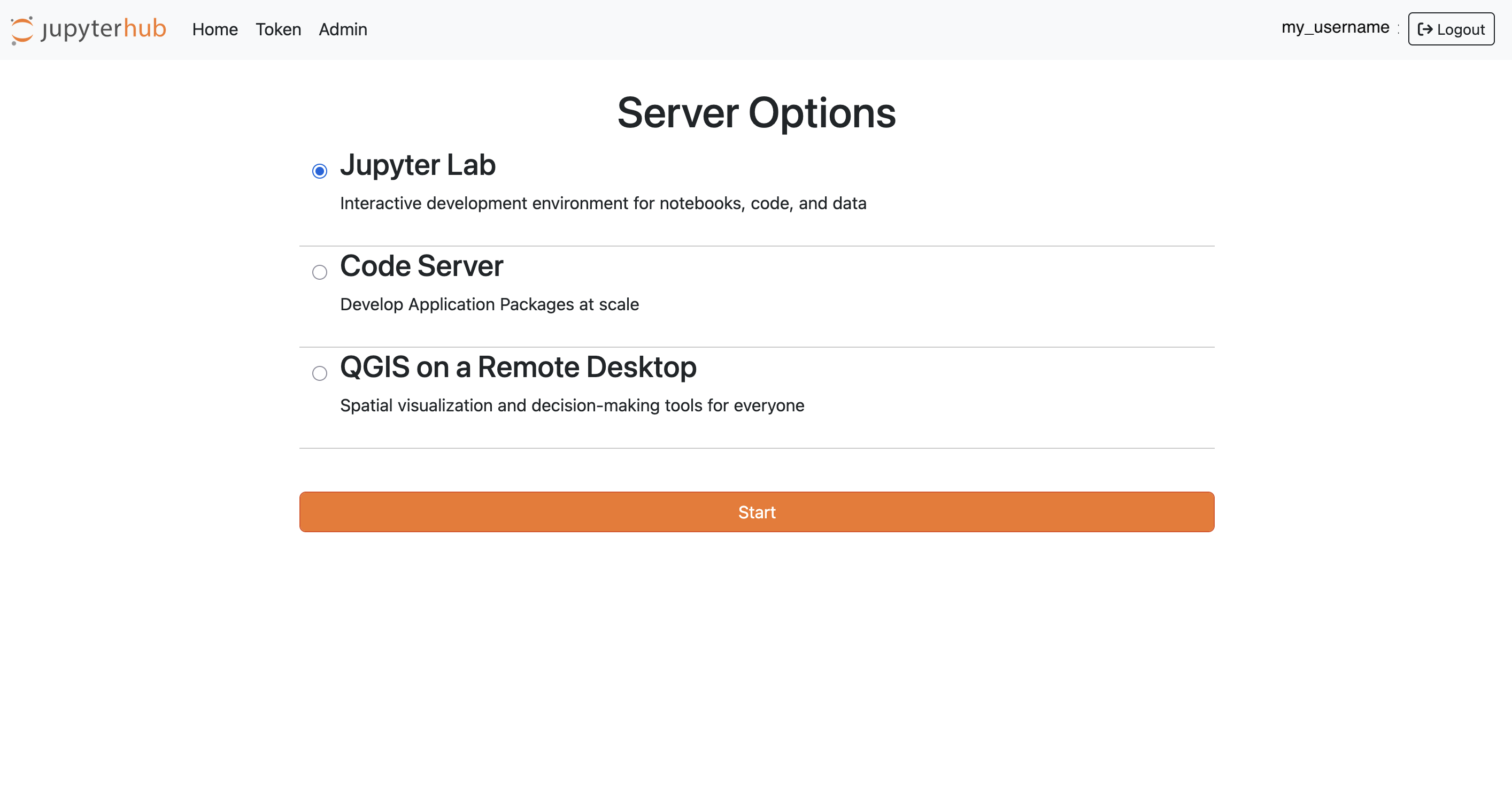
Table 1 showcases example projects that utilize the APEx JupyterLab IDE.
It is important to note that a valid APEx account and permissions from the project are required to access an environment.
| Project | URL |
|---|---|
| APEx (Demo) | https://apphub.demo.apex.esa.int/ |
| SEF - Food Systems | https://apphub.sef-food.apex.esa.int/ |
| SEF - Ecosystems & Biodiversity | https://apphub.sef-ecosystems.apex.esa.int/ |
Additional information will be shared on this page as the project progresses.

