The APEx Geospatial Explorer is a versatile web application designed to visualize and interact with geospatial data. It leverages the OpenLayers library to provide a rich set of features for exploring spatial datasets. The application is highly configurable, allowing users to tailor its functionality and appearance to meet specific project requirements. This document outlines the configuration options for the APEx Geospatial Explorer, detailing the structure and properties of the configuration schema.
Configuration Schema
The service configuration will be based on a schema that provides administrators with the expected structure and contents of the configuration. Taking this approach enables:
- Automated and dynamic instantiation of the service with differing functionality.
- Configuration validation.
- Definition of a “contract” for easier documentation of features and their configuration.
The sections below briefly outline the structure of the configuration schema and provide a preliminary description of each field/property within. The schema currently consists of four top-level fields and all properties are written in camel case.
Layout - layout
An object with properties that modify the elements that the application will render. These properties and elements relate specifically to non-geospatial layout components, like navigation and footer.
Currently supported properties:
Navigation - navigation
An object which supports two properties:
logo: A URL string that points to a logo image asset.title: A string to be used as a title for the application.
Interface Groups - interfaceGroups
An optional array of strings to be used as names/keys. This is currently used to configure the grouping of layer UI elements, such as the layer cards. This will be expanded in later versions.
Exclusivity Sets - exclusivitySets
An optional array of strings to be used as names/keys. This is currently not in use but is a placeholder for future work.
Sources - sources
An array of objects. Each object outlines a particular data source to be configured for display within the application, with properties detailing both the geospatial and user interface configuration.
Currently supported properties within a source object are:
Name - name
A string that is used to identify layers in both the user interface and OpenLayers state
Is Active - isActive
A boolean. Determines if a layer is currently shown on the map. Setting this to true will show the layer on the map when the application loads.
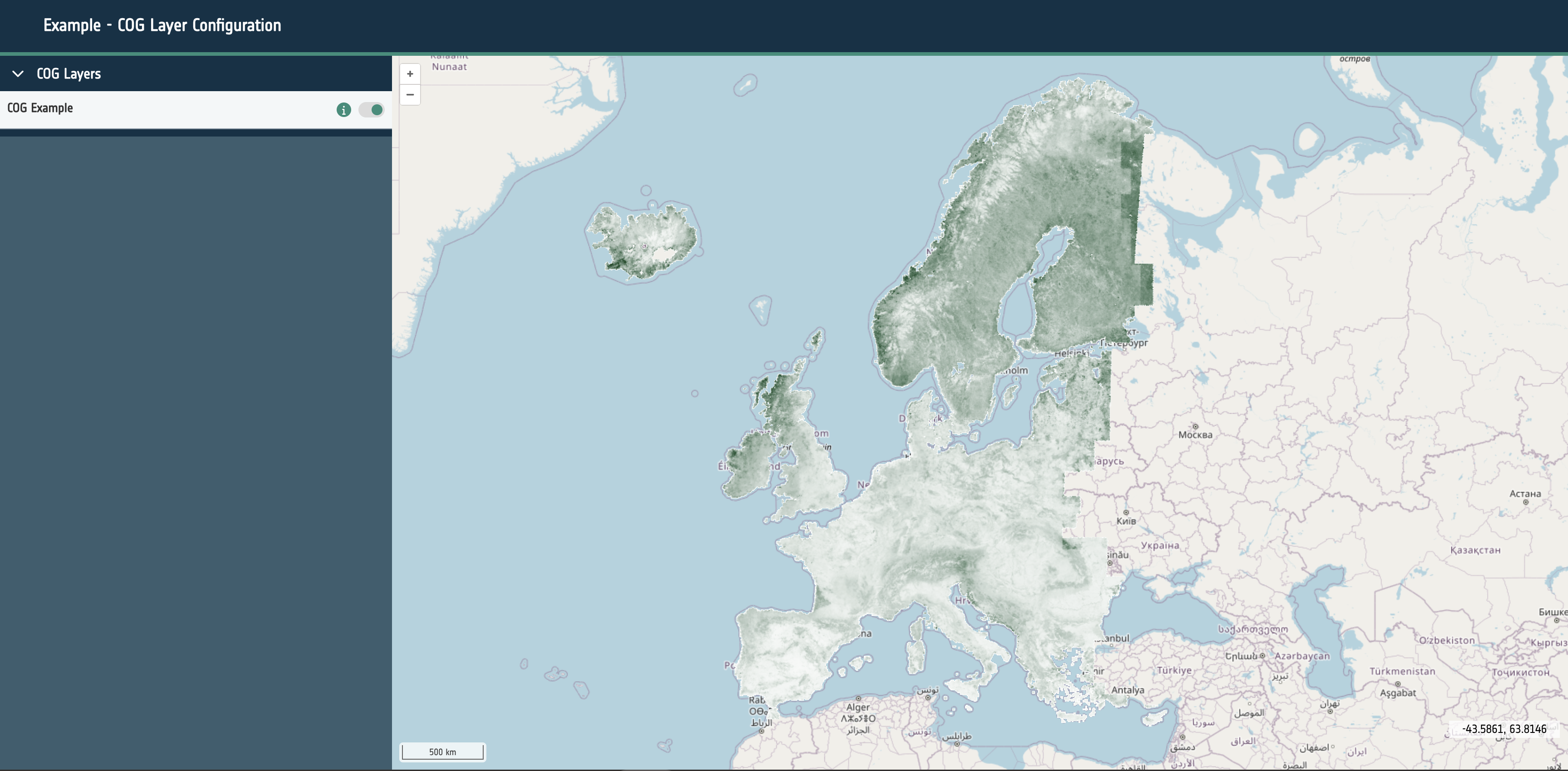
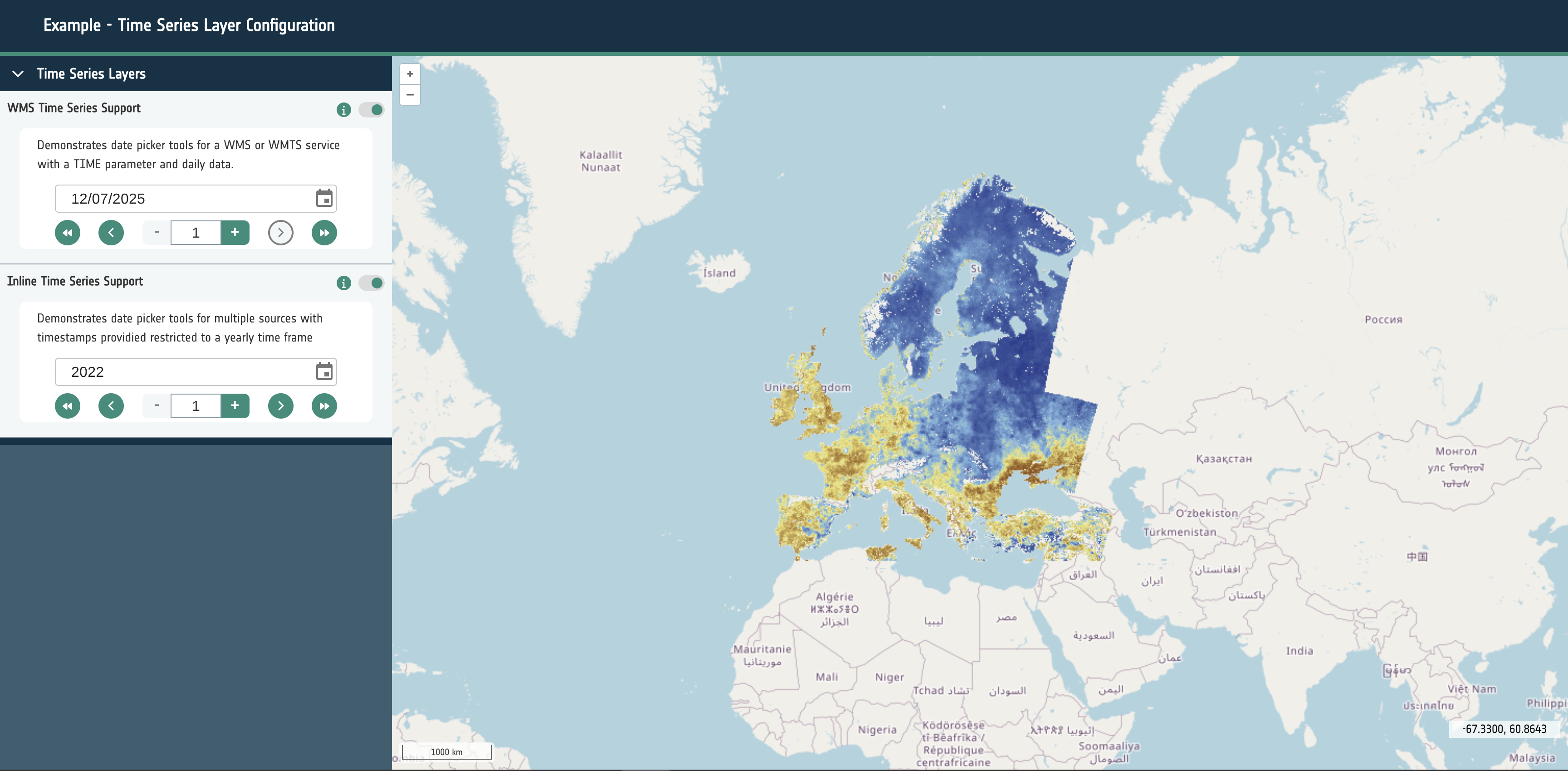
Time Frame - timeframe
A string that is required to render and control time series layers. It should have a value of either Days, Months, Years. This will determine the behavior of the UI for layer groups with time series data configured.
- Days: This will allow the selection of every available date within the configure data sources.
- Months: This will only allow a user to select a the year and the month for the configured sources.
- Years: This will allow only a single year to be selected for the dataset.
For the best user experience it’s essential to set this correctly for the series of datasets in use.
Base Layer - isBaseLayer
Optional boolean that determines if the layer should be treated as a base layer. Base layer groups are always active and cannot be toggled.
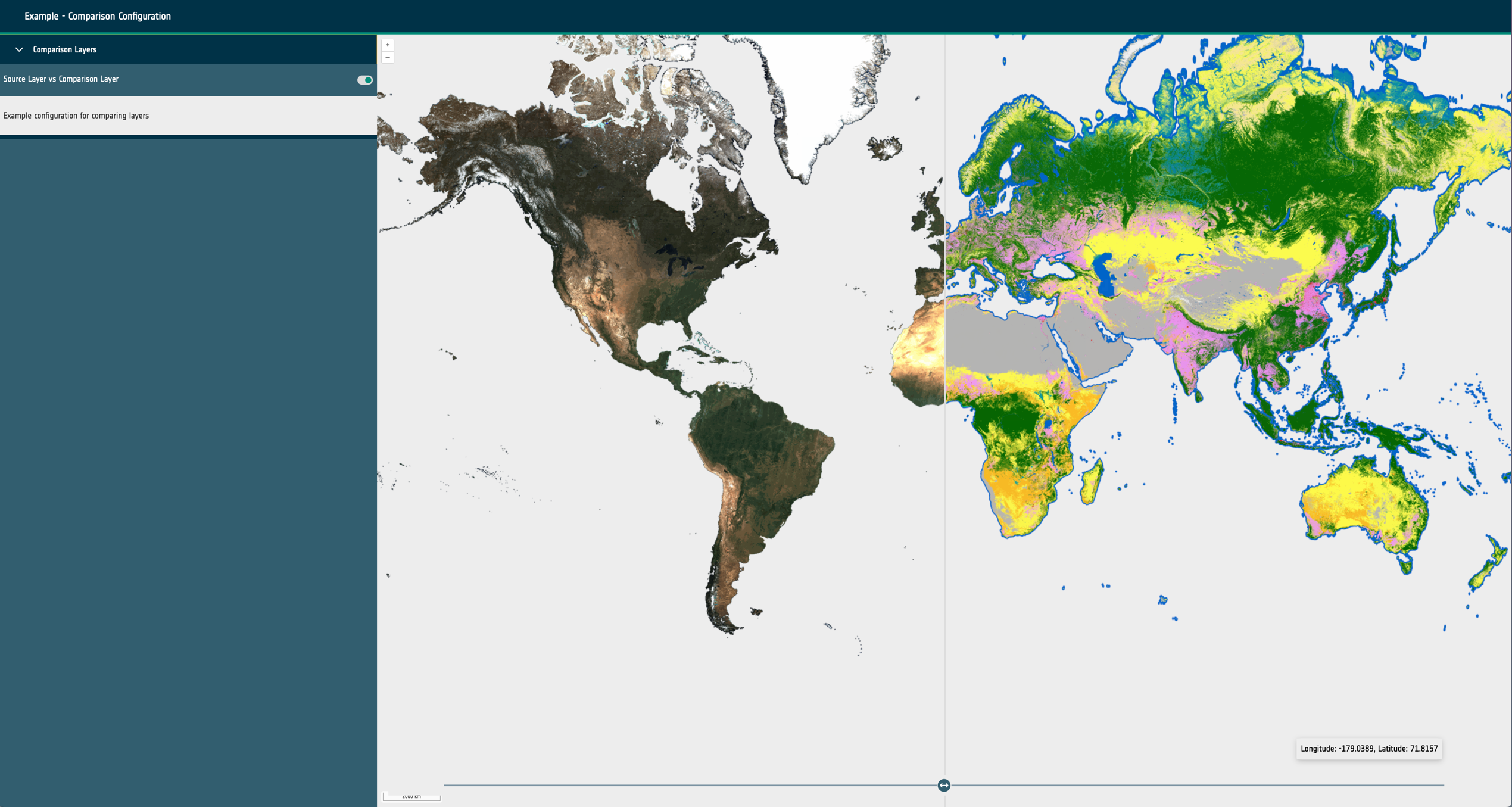
Swipe Layer - isSwipeLayer
Optional boolean that determines if the layer should be treated as a swipe layers. Swipe layer groups are configured much like any other layer group however the individual sources need to be configured with an additional position property with a value of either left or right.
Layout - layout
An object to determine which interface elements are rendered for the layer. Supports two properties:
Layer Card - layerCard
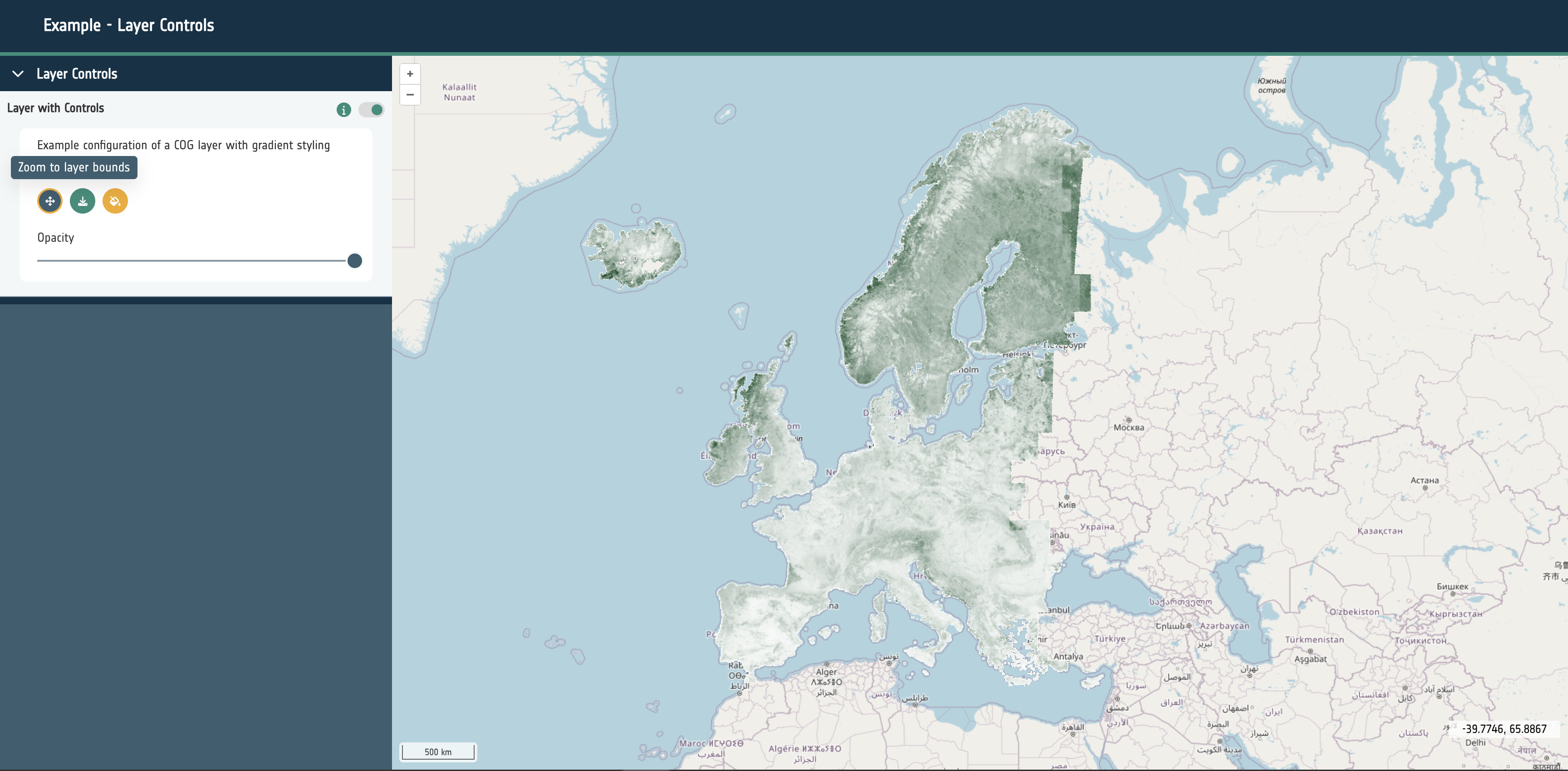
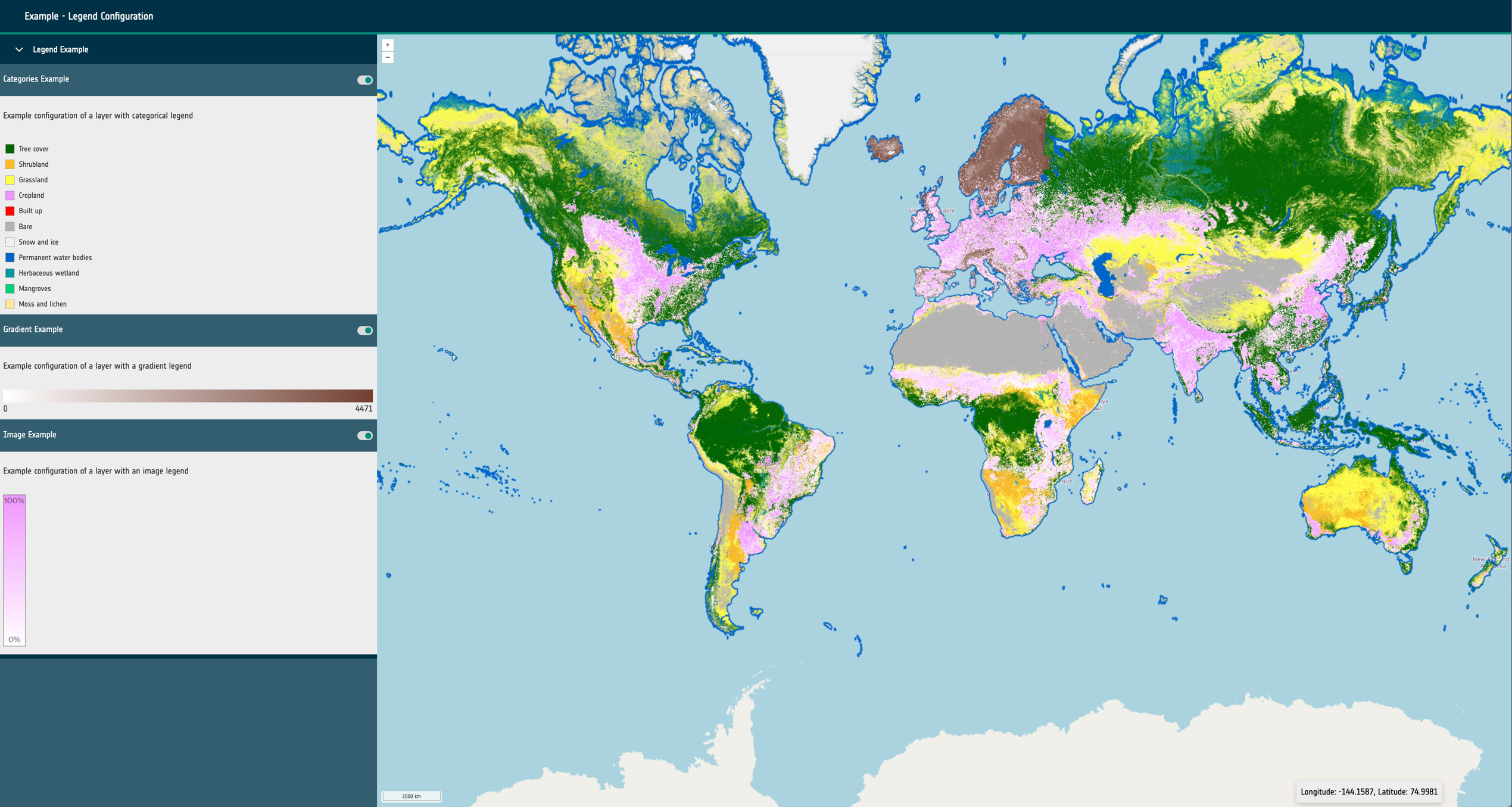
An object that will determine if a layer card should be rendered for this layer and what other interface elements should be rendered within the card. This is currently the main way to interact with a layer within the application. The layer card can show a toggle for the layer, a selection of buttons or controls for the layer, legends and attribution text. This currently supports the following properties:
toggleable: A boolean that determines if a toggle switch to enable/disable the layer should be rendered.controls: An optional object that configures which buttons to render in the layer card for interaction with the layer. This object can contain:
zoomToCenter: A boolean that renders a button that will zoom the map to the extent of the layer.opacitySlider: A boolean that renders a button to open or close the opacity slider control for the layer.download: A URL string that will render a link to the given URL. Used for signposting users to the source data or website.
legend: An optional object that can be configured to show static or dynamic legend elements within the layer card when active. Contains a type property that has a string value of: swatch, image, gradient. Also requires a url property with a string value if the type is image.
Interface Group - interfaceGroup
An optional string that is used to identify which interface group this layer belongs to.
Data - data
An array of objects that configures the data to be displayed in the layer. If the length is more than one a layer group will be created and all sources will be treated as one layer.
Each object currently supports the following properties:
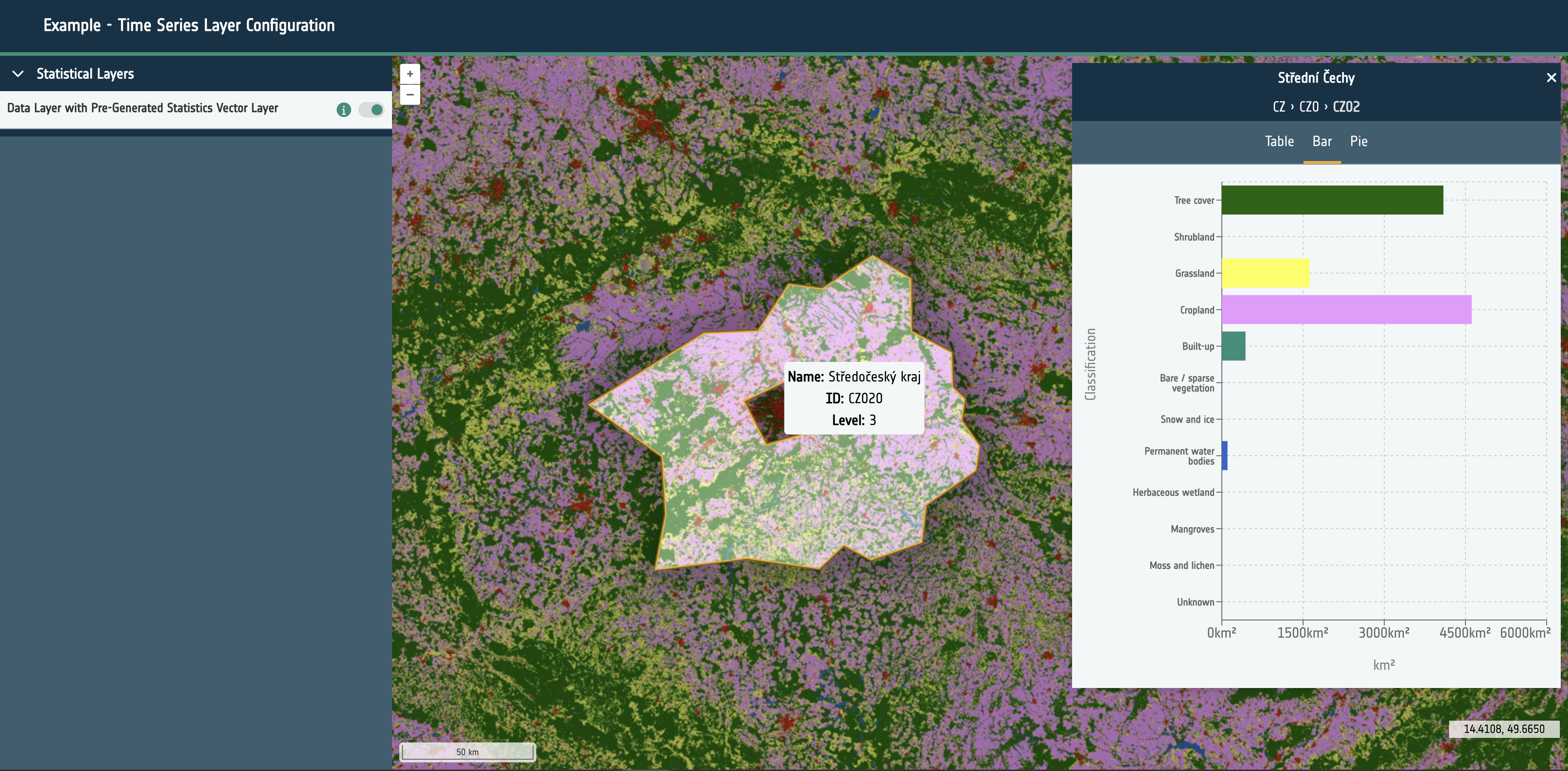
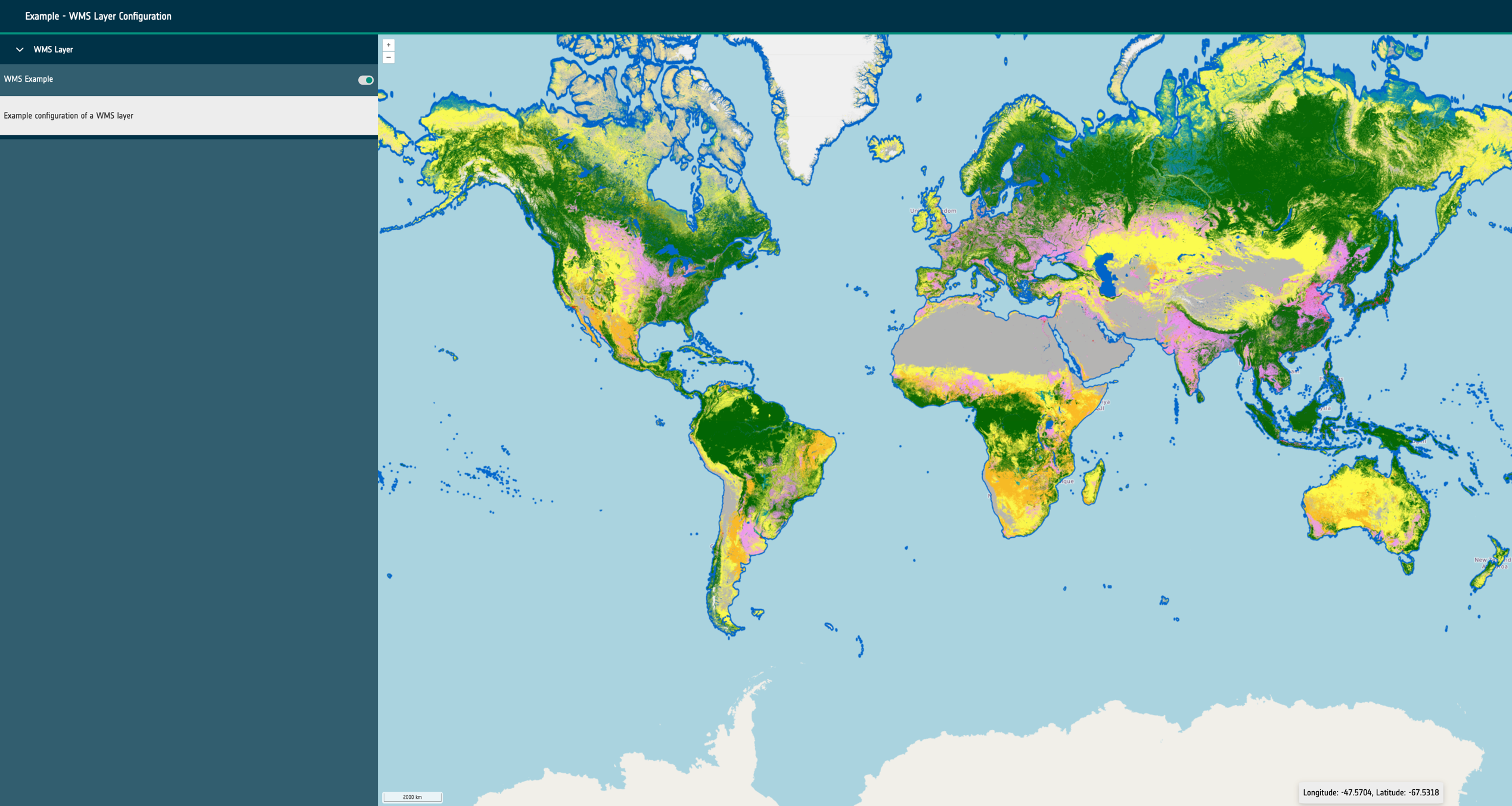
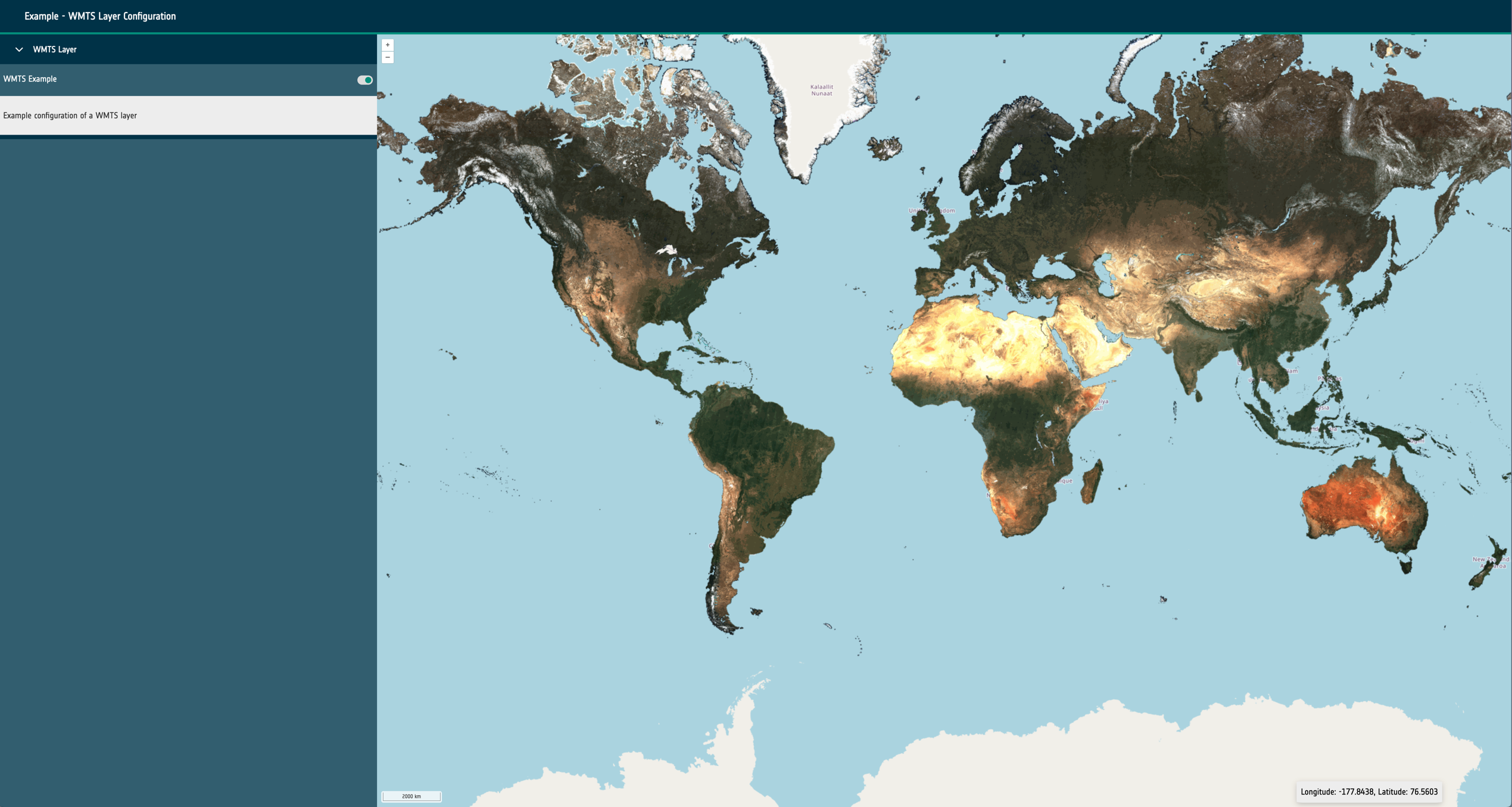
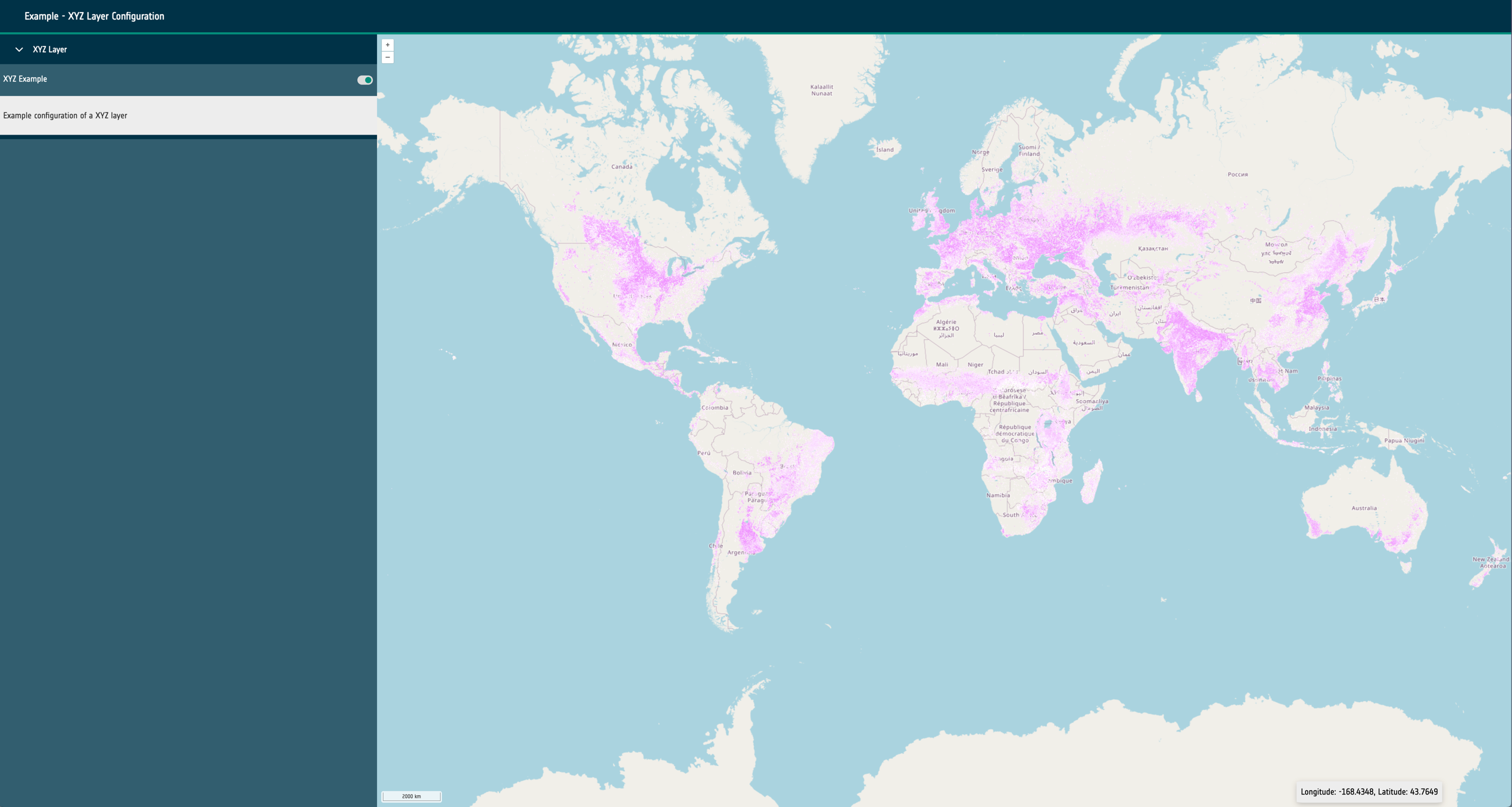
url: A required URL string that points to the dataset’s publicly available resource.format: A required string that identifies what kind of dataset is requested. This can be one of the following: wms, wmts, cog, xyz, wfs, flatgeobuf, stac or geojson.layers: Only required for sources of format: wms and wmts. A string that describes the layer to be requested from the external service.typeName: Only required for sources of format: wfs. A string that describes the type to be requested from the external service.zIndex: Optional integer that determines rendering order within the map. It can be used to override the default rendering of Open Layers.exclusivitySet: Optional string used to identify a group of other layers that should be disabled when this layer is enabled. They must share the same string.projection: Optional EPSG code string that describes the projection of the dataset to Open Layers. If the projection is supported (and doesn’t match the map’s configured projection), it will attempt to reproject the data.style: Open Layers style object that is passed through to the library to modify the rendering of the layer within the map.normalise: Only required for sources of format: cog. Boolean that configures the map to normalise the raster pixel values to between 0 and 1. False by default.level: A required integer for sources of type statistical. Ideally starting at 0, this integer describes the hierarchy of statistical sources. Higher integers should represent more complex and granular vector datasets. Used to provide the statistics feature UI and maintain performance for large vector datasets.position: A string of either left or right that is only required for swipe layer groups. This determines which side of the swipe control the date will be visualised on.timestamps: An optional array of Unix timestamps or ISO8601 date strings. This allows the configuration of time series visualisation within the layer group. If multiple timestamps exist within the layer group and the timeframe property is set a datepicker/stepper control will be rendered to cycle which layer is visible.