Product Catalogue
Overview
The Product Catalogue enables projects to create their own SpatioTemporal Asset Catalogue (STAC), which serves as a comprehensive metadata collection for efficient organisation and discovery of geospatial data assets. This information is presented in a user-friendly JSON format.
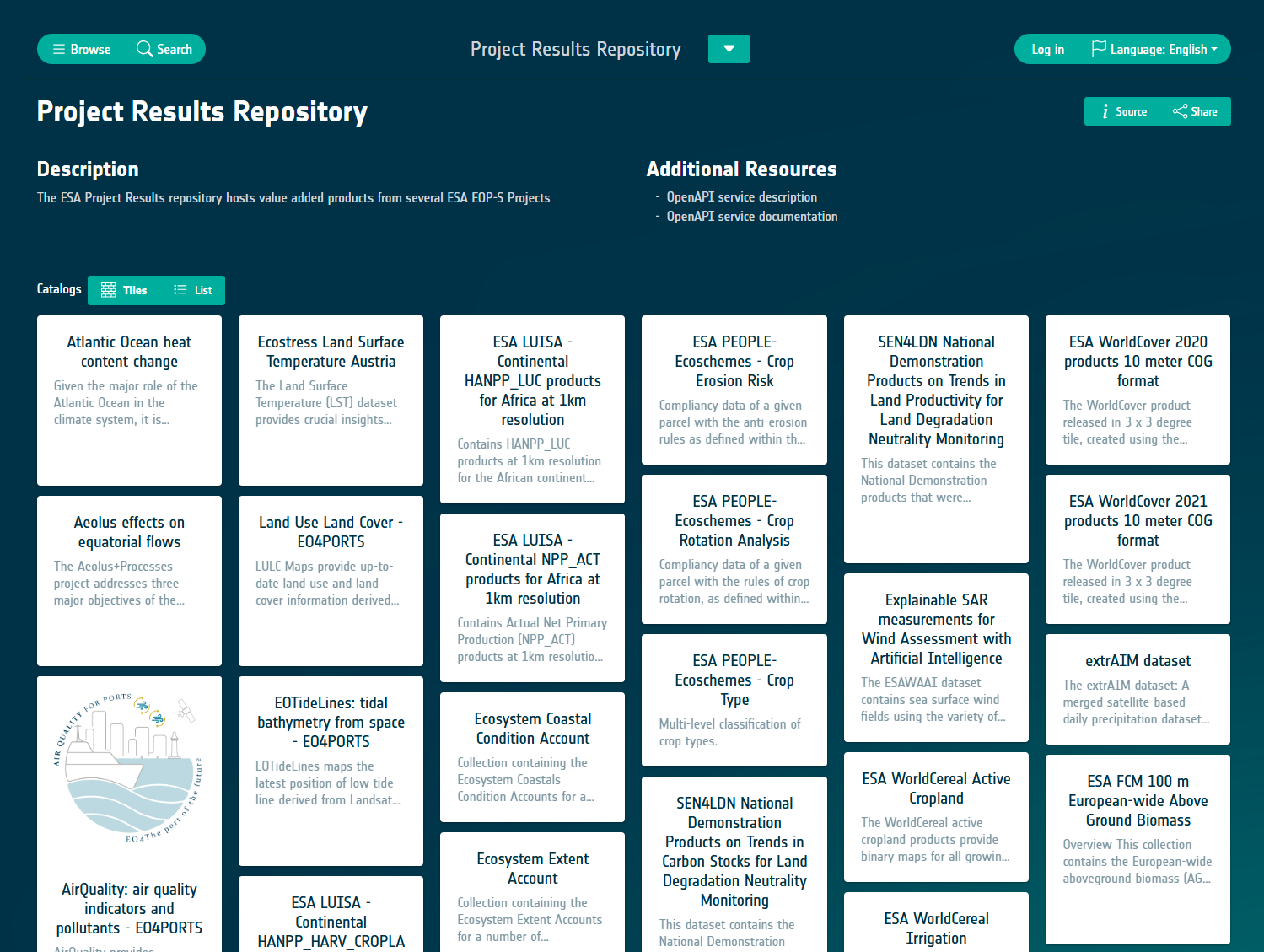
Instantiating a project-specific catalogue gives projects the freedom to use it for a range of purposes, from experimental to operational use cases. Assets that are considered project deliverables will normally be added to the centralised project results repository.
STAC structures data around assets, collections, and catalogues, simplifying search and access based on attributes such as time, location, and other metadata. The concept of a STAC catalogue emphasises simplicity, operating as a REST-based web service with a single HTTP endpoint for communication. This API-centric design ensures easy integration into existing applications and tools, including other APEx services.
Showcase Scenarios
The product catalogue serves several beneficial scenarios for projects:
Data Accessibility
The service offers easy access to a wide range of geospatial data sources, enabling project teams to quickly locate and utilise relevant data without the need to manage large datasets locally.Tool Integration
By adhering to the STAC standard, the service enhances interoperability among different data sources, software tools and processing platforms such as openEO and OGC Application Packages. This ensures seamless integration of datasets from various providers, supporting comprehensive analysis and decision-making. This interoperability extends to other APEx tools such as the Geospatial Explorer, Code Server IDE, JupyterLab IDE, ….Efficient Search and Discovery
Users can efficiently search and discover datasets based on specific criteria such as time, location, and data type. This capability streamlines research, planning, and operational tasks by providing quick access to relevant information.Enhanced Collaboration
The service promotes collaboration by providing a centralised platform where project stakeholders can access and share geospatial data and analyses. This collaborative environment fosters innovation and knowledge sharing across disciplines and organisations.
What does APEx offer?
STAC Catalogue API
You will get a dedicated STAC catalogue, hosted and managed by APEx. This gives you full control over the metadata, without having to worry about IT aspects such as security, backup or monitoring the service. The catalogue supports creating both private and public collections.
Key Considerations
- Data storage: The STAC catalogue does include limited data storage. It is recommended to request object storage access from one of the cloud providers in the Network of Resources (NoR).
- Metadata Creation: The process of creating metadata is not automated. You will need to provide the metadata in JSON format, giving you complete flexibility in choosing the STAC extensions that best suit your requirements.
Underlying Technology
- Software: The catalogue is powered by stac-fastapi-elasticsearch-opensearch.
- Database: It uses a managed OpenSearch instance hosted on Open Telekom Cloud.
While the APEx team handles software upgrades when necessary, please note that support for custom software development is not provided.
STAC Browser
In addition to the STAC Catalogue API, APEx provides a dedicated STAC Browser to support the visual exploration of your catalogue’s content. This browser is seamlessly integrated with the instantiated API and is automatically configured upon initialization to display the results published in your STAC API.

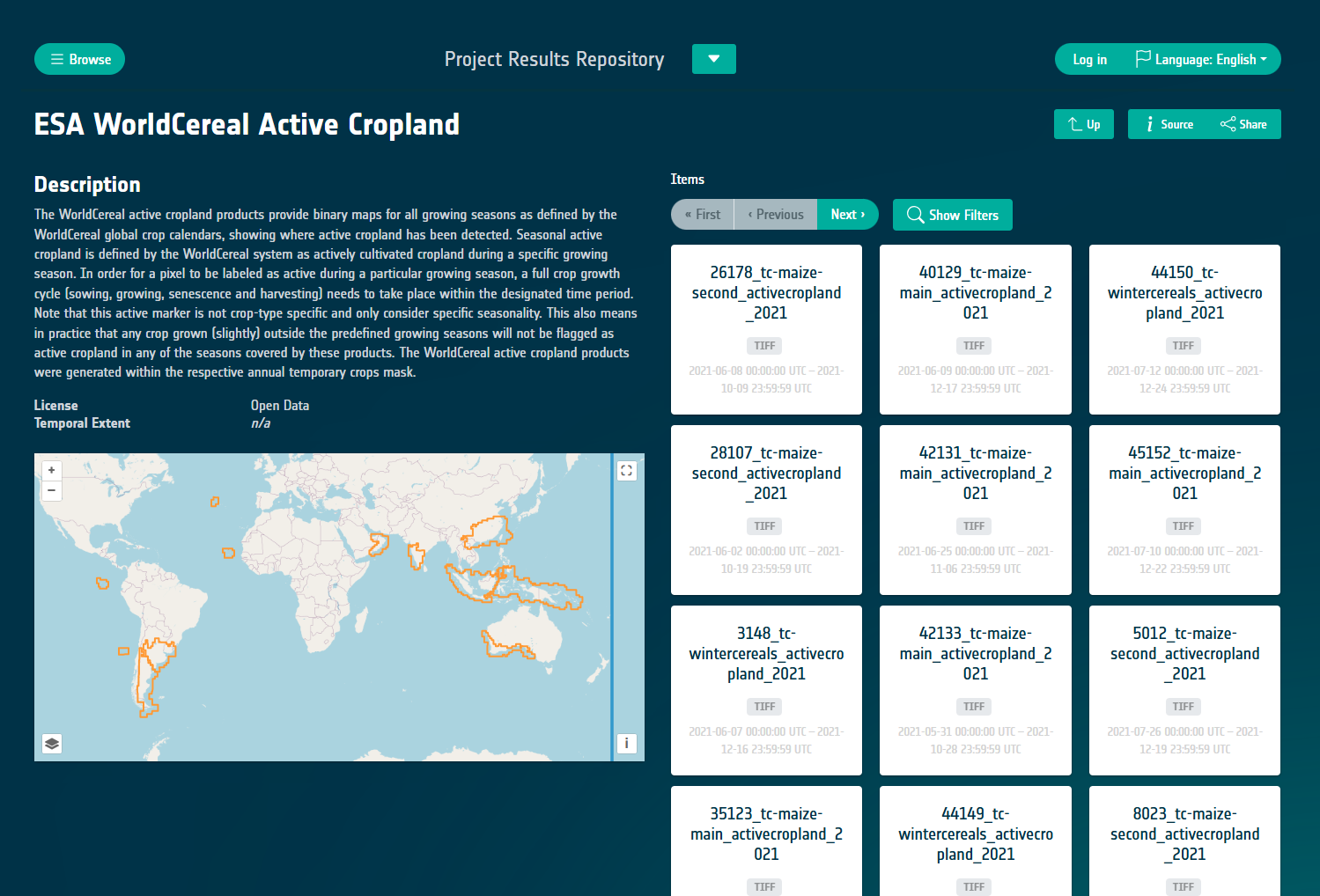
Underlying Technology
The STAC browser is built on the well-known Radiant Earth’s STAC browser, an open-source project designed to enable interactive exploration of STAC catalogs. This web application can be customized to meet specific user needs, offering flexibility for a wide range of applications.
How to integrate the catalogue in your project architecture
The role of the STAC catalog, is in essence to facilitate data discovery and exchange between different components in your project. By the use of a shared metadata language, components can be decoupled and still work together. It allows different project partners also to work together, even if they use different software stacks.
We list some common cases below.
Data set viewing
Data viewing is one of the most basic use cases. Most viewer implementations traditionally require to ingest data in a viewer specific database. However, when metadata is sufficiently rich, and the viewer understands STAC, it can directly query the STAC catalog, as long as it’s sufficiently responsive for the low latency requirements of the viewer.
Data processing
In the most basic case, a processing component simply stores final products in the catalog. Sufficiently advanced processing systems will immediately generate STAC metadata, and may even allow writing into the catalogue API directly. They also record data provenance, which is a key aspect of FAIR data principles.
In a more advanced case, the processing workflow requires storing intermediate products, or preprocessed ancillary data sets. Also then, the STAC catalogue can be used to keep track of these data sets. By doing so, the processing component can simply read required inputs from STAC, and store (intermediate) results back into the catalog.
Machine learning datasets
A more advanced but increasingly common use case is to use a catalogue to track reference data sets, as well as training patches in a STAC catalog. Here we again have a pattern where various components like the EO processing system, model training scripts and reference data management system all work together around a central metadata store.
Guides
The following guides showcase how you can interact with the catalogue API:
Examples
Table 1 showcases example projects that use the APEx Product Catalogue:
| Project | URL |
|---|---|
| APEx | https://browser.apex.esa.int |
| APEx (Demo) | https://browser.demo.apex.esa.int |
| World Ecosystem Extent Dynamics (WEED) | https://browser.weed.apex.esa.int |
Additional information will be shared on this page as the project progresses.

